
uMETHOD Health has implemented a precision-medicine platform to create personalized, multidomain care plans for the treatment of dementia and mild Alzheimer disease.

uMETHOD Health has implemented a precision-medicine platform to create personalized, multidomain care plans for the treatment of dementia and mild Alzheimer disease.

The AMBAR trial is based off of the hypothesis that amyloid-beta is bound to albumin and circulates in plasma; extracting this plasma may in turn flush amyloid from the brain.

Lead author Elizabeth K. Seng, PhD, shared insight into the findings of an exploration of the use of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy to reduce the impact of migraine on patients, as measured by Migraine Disability Assessment, as well as Headache Disability Inventory scores.

The professor of emergency medicine at the University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health spoke about how telemedicine in senior living communities can effectively decrease ED use by individuals with dementia.

The concept of cognitive reserve refers to one’s capacity to be resilient to age-related brain degeneration and disease-related pathology.

People who did not use trazodone had up to a 2-fold faster decline in MMSE score than those who used the drug.

The International Congress on the Future of Neurology will take place this Fall in New York City, converging experts in neurology to discuss the latest data and best practices to better inform clinical decision-making.
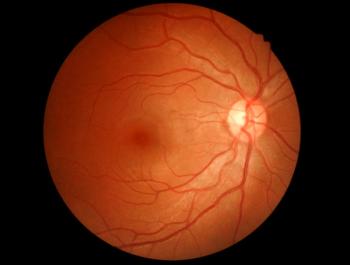
Six months after delivering a healthy baby girl, a physician experiences intermittent blurred vision and tingling in her left leg. Her diagnosis might surprise you.

Findings suggest that a subgroup of patients categorized as amyloid beta-negative may continue to accumulate the destructive protein and experience cognitive changes.

The research fellow at the University of Exeter spoke about the findings from her observational study which showed that living a favorable lifestyle could offset the risk for dementia, even if that risk is genetically linked. 



While single modality therapy is safe, feasible, and effective, researchers demonstrated that a combined modality shows greater domain-specific cognitive enhancements with higher transferability and sustainability.

Participants with high CSF Aβ1-42/tau and lower NPTX2 levels experienced greater decline throughout the 36 months than all other subgroups on memory acquisition, delayed recall, and CDR-sb.

Investigators found that participants struggled to adhere to the treatment protocol, which required them to administer 3 treatments per day.

The director of headache medicine and chief of general neurology at Yale Medicine spoke about the significance of having CGRP inhibitors in migraine treatment, and how eptinezumab fits into the treatment landscape.

No differences were observed in the magnitude of ubrogepant treatment effect between defined triptan subgroups.

The clinical professor of neurology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine spoke about the trends revealed by the OVERCOME study, and how this data can be used to improve the management of the millions of patients with migraine in the US.

The director of the Montefiore Headache Center and professor of neurology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine spoke about the results of an analysis of eptinezumab’s effect on the severity of migraine and its impact on patients’ lives.

Atogepant significantly reduced mean monthly migraine days compared to placebo across a number of doses and was generally well-tolerated, with no treatment-related serious adverse events.

Real-world data of erenumab indicates that a large number of patients are the chronic migraine population, and there is a high rate of persistence to the anti-CGRP therapy. The most commonly prescribed dose of erenumab was 70 mg.

Patients with migraine who reported both moderate and severe pain intensity during headache attacks experienced high rates of relief and freedom from pain and their most bothersome symptom when treated with 3-mg sumatriptan injection, DFN-11.

Neurology News Network for the week ending July 13, 2019.

An analysis of the open-label PREVAIL trial demonstrated a magnitude of therapeutic effect for eptinezumab that was either maintained or improved with subsequent infusions.

The professor of neurology, neurotherapeutics, and ophthalmology at UT Southwestern spoke about the potential of telemedicine in headache medicine, as well as the findings from a single-center, 45-patient study.

Despite ongoing discussion regarding the 6-item Headache Impact Test’s relevance in the migraine population—for which it was not specifically developed—the test has been shown to be a useful tool in the assessment of patients with migraine.

The director of the MedStar Georgetown Headache Center spoke about ubrogepant’s long-term safety and efficacy and its potential to fill the large gap that remains in acute migraine care.

All doses of Staccato alprazolam reduced the standardized photosensitivity range at 2 minutes; the effect was sustained for the 0.5 mg dose through 4 hours and 6 hours for the 1 mg and 2 mg doses.

Patients with migraine rated their telemedicine visits as more convenient with shorter visit times; two factors that can also benefit providers.

The group’s goal is for the clinical research community to develop an accurate, precise clinical test to predict brain injury recovery after resuscitation from cardiac arrest.

Survey data revealed 36% of patients with migraine with prescription medications were using opioids in acute management, though data also reinforced that receiving a diagnosis of migraine or chronic migraine was associated with a significantly decreased likelihood of opioid use.

As measured with the Migraine Disability Assessment, the proportion of patients with episodic migraine experiencing severe disability was reduced significantly, and Headache Disability Inventory scores were significantly reduced.