
The findings from an analysis of more than 2000 plasma samples suggest that levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, independent of APOE, are associated with early-onset Alzheimer disease—and that the APOB gene may play a role.


The findings from an analysis of more than 2000 plasma samples suggest that levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, independent of APOE, are associated with early-onset Alzheimer disease—and that the APOB gene may play a role.

Results of the large, long-term, population-based study suggest that statin therapy in older adults who experience a concussion may help reduce the deleterious effects of brain injury.

The WHO guidelines specifically promote a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, not smoking, avoiding the harmful use of alcohol, maintaining a healthy weight and diet, and keeping healthy levels of blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar.

How are you counseling patients and families about the risks and benefits of playing sports with repetitive head blows and the risk of CTE?
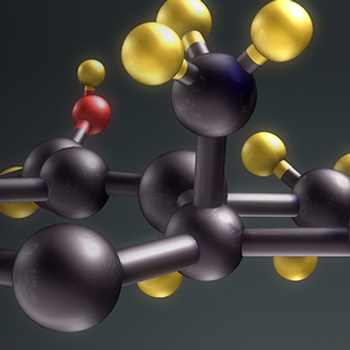
Suvorexant improved the mean total sleep time by 28.2 minutes for the patients receiving the treatment versus placebo, equating to a mean increase of 73.4 minutes with the orexin receptor antagonist.










The chief medical officer and head of Research & Development at Ovid Therapeutics spoke about the Visual Analog Scale that the company developed to help better understand the impact that potential treatments have on patients with Fragile X syndrome.

The post hoc analysis pooled data from 3 trials to evaluate the benefits of adding memantine to treatment with cholinesterase inhibitors for patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer disease.

The report includes consensus-based recommendations, which consist of guidelines for the diagnosis and staging of LATE-neuropathological change—defined by stereotypical TDP-43 proteinopathy both with or without simultaneous hippocampal sclerosis pathology, in older adults.

Researchers found that cognitively unimpaired patients with apneas had an average of 4.5% higher levels of tau in the entorhinal cortex than those who did not have apneas, after controlling for several other factors.

A prospective case controlled study looked at the relationship of retinal blood flow and vessel density to early onset Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment.

The adoption of plasma NfL as a biomarker for tracking neurodegeneration would help fill a need for a less invasive, more economical biomarker.

What do you suspect is responsible for this patient’s progressively worsening cognitive symptoms?

NeurologyLive spoke with the director of the Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health to learn why, despite hundreds of failed trials and therapies, there is growing excitement for what's to come.

Research from the past decade suggests that sigma-1 receptors and their encoding gene, SIGMAR1, together act as a therapeutic target for patients with dementia.